June 1, 2023
The Importance of Rapid Prototyping in Modern Engineering
POSTED BY
Team STUFF USA
Modern advancement is all about improving work efficiency, eliminating errors, and being accurate and productive. When it comes to being sure about your product and results – prototyping is a great way of being affirmative of your designs. Among the many advancements in modern engineering, rapid prototyping is one of the most effective.
Today we are going to discuss in detail all the whereabouts of rapid prototyping. Let’s start by exploring each segment:
What is Rapid Prototyping?
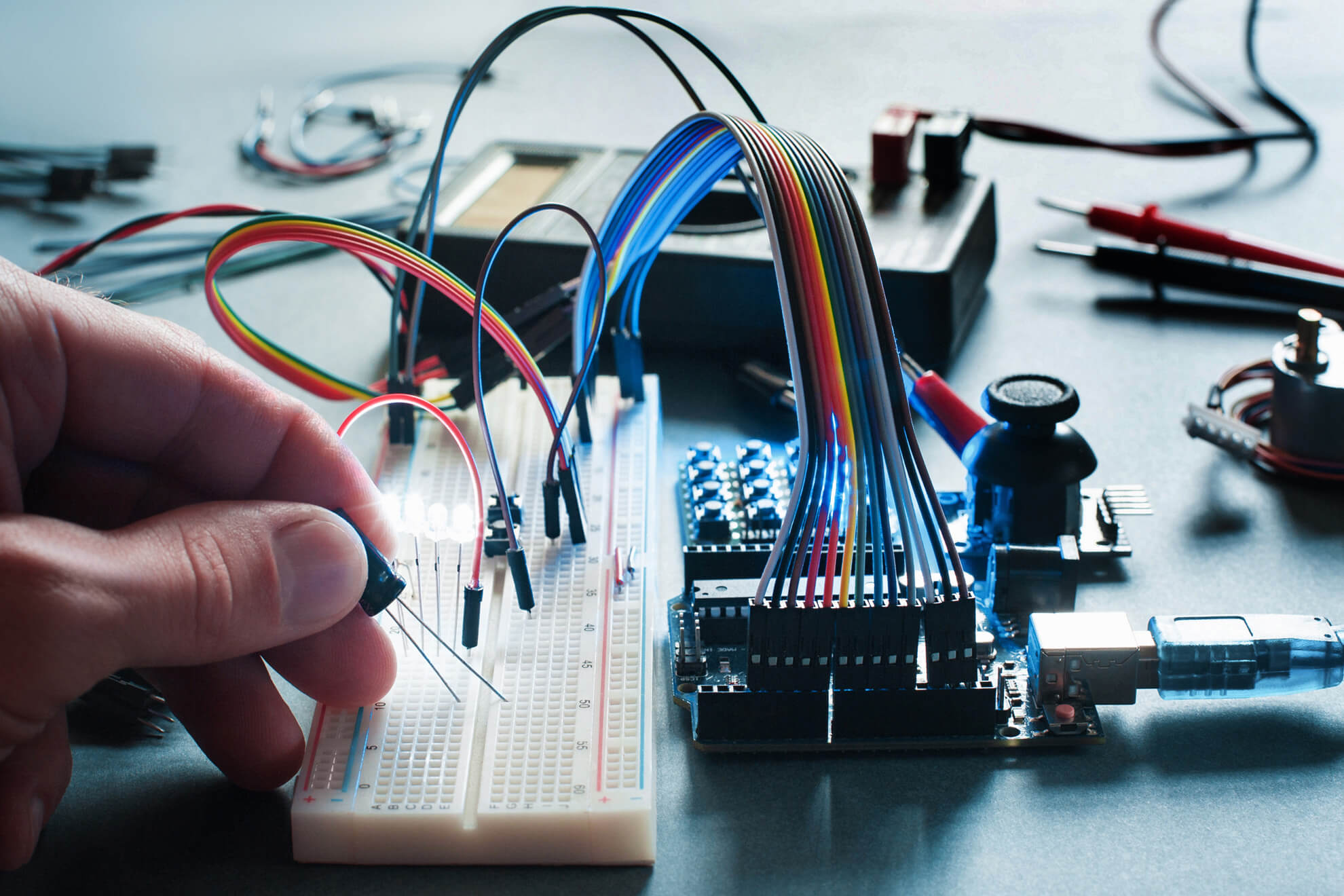
Using 3D computer-aided design (CAD), rapid prototyping is the quick creation of a physical part, model, or assembly. Typically, additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is used to create the item, model, or assembly.
A high-fidelity prototype is one in which the design closely resembles the planned finished product, as opposed to a low-fidelity prototype, which differs significantly from the final product. Although a number of manufacturing technologies are used in rapid prototyping (RP), multilayer additive manufacturing is the most common. However, high-speed machining, casting, molding, and extrusion are some additional technologies employed in RP.
Key Benefits of Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping helps you to stay ahead of time. It gives you a clear vision, helps to estimate project time, etc.
Now let us analyze the benefits of rapid prototyping below:
• Accelerated product development:
As the name suggests, Rapid prototyping allows the creation of prototypes swiftly. This feature helps to save a lot of time and accelerate the whole process which makes it easy to innovate ahead of new ideas and other products.
The fast process of rapid prototyping helps to create feedback loops. Now these loops help to not only identify the errors but also rectify them timely. This helps to create an early approach. If errors or missouts are detected ahead of time, then it gives way more time to refine the final product even more.
• Cost savings and risk reduction:
Prototyping of the product helps in saving a lot of time and extra costs. Usually, when products take time to execute, additional cost and time is spent on them. This can be a revenue leakage, cost hampering is not favorable for any business.
With the help of rapid prototyping, one doesn’t need to be exhausted from all the extra time and cost drainage.
• Enhanced collaboration and communication:
Rapid prototypes offer a visual and interactive representation of ideas, making it easier for stakeholders to provide feedback and validate concepts. This visual aspect enhances communication and ensures that everyone is on the same page regarding the product’s design and functionality.
Techniques and Technologies for Rapid Prototyping
3D Printing
A manufacturing technique known as 3D printing uses layer-by-layer construction to turn digital CAD files into physical items. One of the many applications of 3D printing is rapid prototyping.
3D printing offers several advantages, including rapid turnaround time, the ability to create complex geometries, customization options, and cost-effective production for small batches. However, it also has limitations such as limited material choices, lower strength compared to traditional manufacturing methods, and the need for post-processing in some cases.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
CAD software allows engineers to create detailed digital models of products or systems. It provides tools for designing, visualizing, and simulating the behavior of the product. CAD enables rapid prototyping by allowing engineers to quickly iterate and refine the design in a digital environment.
The iterative design process involves making design changes, simulating performance, analyzing functionality, and refining the design based on the results. This iterative approach helps in rapid prototyping and reduces the time and cost associated with physical prototyping.
Virtual Prototyping
Virtual prototyping involves creating computer simulations to test the performance, functionality, and behavior of a product or system. It allows engineers to simulate real-world conditions, analyze the impact of different factors, and optimize the design virtually. Virtual prototyping helps in identifying design flaws and making informed decisions before physical prototyping.
Engineers can use virtual simulations to refine the design and then create physical prototypes for further validation and testing. This integration enables a more efficient and cost-effective prototyping workflow, reducing the number of physical iterations required.
Applications of Rapid Prototyping
Metal or plastic components can now be prototyped and produced quickly. Prototypes in full color can also be made. Rapid prototype techniques including stereo lithography (3D printing), selective laser sintering, ColorJet printing, direct metal printing, fused deposition modeling, and even CNC machining alternatives can all be used by manufacturers using computer data.
Concept models can be produced using various 3D printing and fast prototyping techniques. A physical concept model is more effective than a virtual one at explaining concepts to designers, engineers, and other stakeholders. It is possible to construct functional prototypes that include every design element and enable in-depth testing before full production is planned. A product’s functionality and manufacturability, as well as how well the parts fit together, can all be evaluated.
Manufacturers can assess if they’ve accomplished the functionality and aesthetic design they anticipated once a working prototype is available. They can determine whether it is economically feasible to continue with production. Everything from basic plastic or metal pieces to computer circuitry and electric car components is made using this method.
Challenges faced in Rapid Prototyping
- One of the challenges in rapid prototyping is the limited range of materials available for certain techniques. Different prototyping methods may have specific material requirements, and not all materials may possess the desired properties for the final product.
- Rapid prototyping aims to expedite the product development process, but there can be a trade-off between speed and quality. Rushing through iterations or cutting corners may compromise the accuracy and reliability of the prototype. It is crucial to strike a balance between speed and quality by ensuring that each iteration is thoroughly tested and meets the required standards.
- Rapid prototyping involves sharing design files and collaborating with different parties. This raises intellectual property concerns, as unauthorized replication or disclosure of sensitive designs can occur. Companies and individuals must take measures to protect their intellectual property by implementing appropriate security measures, using non-disclosure agreements, and carefully managing access to design files during the prototyping phase.
Possibilities of the Future in Rapid Prototyping
- Future trends in rapid prototyping involve the development of new materials and fabrication techniques. Researchers are continuously exploring and improving materials with enhanced properties such as strength, durability, and conductivity.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are expected to play a significant role in the future of rapid prototyping. AI algorithms can aid in design optimization, automatically generating design variations, and suggesting improvements based on predefined criteria.
- As rapid prototyping technologies mature, there is a trend toward increased accessibility and affordability. Costs associated with equipment, materials, and software are gradually decreasing, making rapid prototyping more accessible to a wider range of users.
Conclusion
Post discussing the importance of rapid prototyping one can ascertain that it is one of the fastest manufacturing technologies. Making it possible for mechanical engineers, product designers, and development teams to visualize complicated forms that are difficult to perceive on connectional drawings and validate their concept ideas.
Additionally, early or late design stages might take advantage of quick prototyping and rapid tooling to create a conceptual model or make changes to the specifics before the prototype is put into mass production.
Even though many businesses have already seen the value of these technologies, expect to see fast prototyping become a common manufacturing technique among many design teams. Also, to further scale down models and mechanical components in conjunction with conventional production techniques.