October 1, 2023
Demystifying Injection Molding: A Comprehensive Guide
POSTED BY
Team STUFF USA
Injection molding is a manufacturing process that lies at the heart of countless products we encounter daily, from the plastic components in our smartphones to the intricate parts of our automobiles. While it operates quietly behind the scenes, understanding injection molding is pivotal in today’s manufacturing landscape. In this comprehensive guide, we will unveil the intricacies of injection molding, breaking down its processes, materials, and applications. Whether you’re an industry professional looking to deepen your knowledge or an enthusiast eager to explore the world of manufacturing, this guide will empower you with the insights needed to grasp the magic behind injection molding.
The Importance of Understanding Injection Molding in Manufacturing
Injection molding is a manufacturing technique that transforms raw materials, typically plastics and polymers, into an astonishing array of products. Its significance in modern manufacturing cannot be overstated. The ability to create intricate, high-quality, and cost-effective components at scale has made injection molding an integral part of industries ranging from automotive and electronics to medical devices and consumer goods. It’s the technology that makes mass production of complex designs not just possible but efficient.
This guide is designed to be your go-to resource for comprehending injection molding. We will delve deep into the process itself, from the moment raw materials are loaded into the machine to the final quality control checks. We will explore the materials used, the design considerations that can make or break a project, and the types of machines that make it all happen. Moreover, we will discuss quality control, troubleshooting common issues, and even the exciting innovations and trends shaping the future of this industry.
Whether you’re a seasoned professional or someone with a burgeoning interest in manufacturing, this guide will equip you with a comprehensive understanding of injection molding. By the end of it, you’ll appreciate how this seemingly arcane process plays a pivotal role in the products that enrich our lives daily.
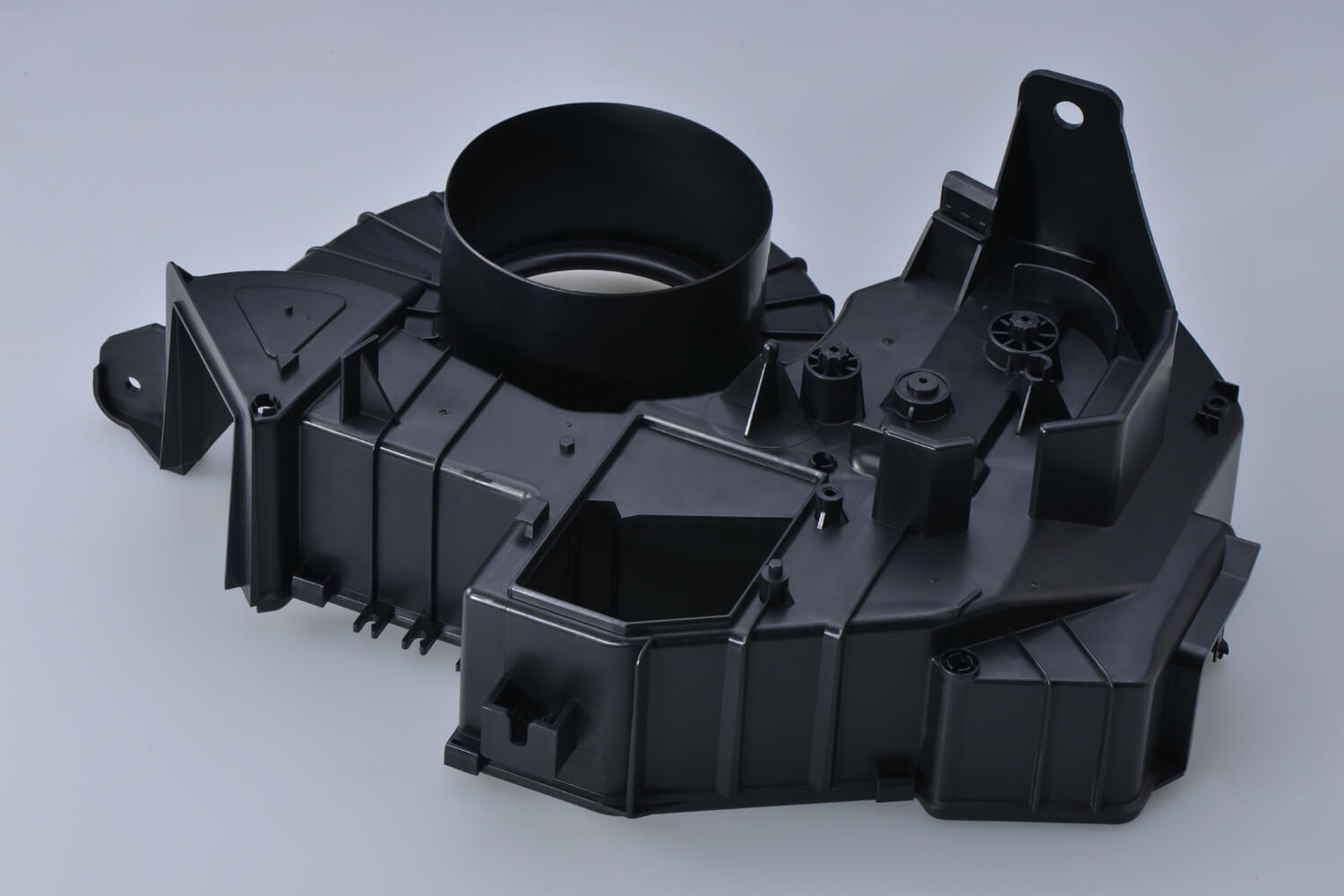

What Is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a versatile and widely used manufacturing process that involves the creation of three-dimensional objects by injecting molten material, typically plastic, into a mold cavity. Once the material cools and solidifies within the mold, it takes on the desired shape, forming anything from intricate consumer product components to large industrial parts.
The significance of injection molding in modern manufacturing cannot be overstated. It stands as a cornerstone of the industry, enabling the production of high-quality, precise, and intricate components on a mass scale. This method revolutionized manufacturing by offering cost-effective solutions for creating complex shapes and intricate designs. Injection molding’s ability to produce parts with consistency, speed, and minimal material waste makes it a go-to choice across various sectors, from automotive and electronics to healthcare and consumer goods.
The Injection Molding Process
Injection molding is a precise and highly structured manufacturing process that involves several distinct steps. Each of these steps is crucial in the creation of high-quality parts. Let’s take a detailed look at each phase of the injection molding process:
Mold Clamping
The injection molding process begins with mold clamping. In this phase, the two halves of the mold, known as the mold cavity and mold core, are securely closed and held together by the clamping unit of the injection molding machine. The clamping unit exerts a significant force to ensure the mold remains tightly shut.
Proper mold clamping is essential for several reasons
It prevents material leakage during the injection phase by ensuring a tight seal.
• The clamping force applied determines the final shape and dimensions of the part, ensuring precision and consistency across multiple production runs.
• Effective clamping prevents flash, which is excess material that can form along the parting line if the mold is not securely closed.
Injection
The injection phase is where the magic happens. It involves the introduction of raw material, typically in the form of small pellets or granules, into the injection unit of the molding machine. Inside the unit, a reciprocating screw rotates and moves forward to heat, melt, and homogenize the material. Once the material is in a molten state, it is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure.
Injection is a critical step because
• It shapes the material into the desired geometry, taking on the intricacies of the mold.
• The injection process controls the flow rate and pressure, ensuring the material reaches all corners of the mold, preventing defects such as voids, air pockets, or incomplete fills.
• Uniform filling of the mold ensures consistent quality and repeatability across all parts produced.
Cooling
After injection, the mold remains closed, allowing the molten material to cool and solidify. Cooling channels strategically placed within the mold help regulate the temperature during this phase.
Cooling is crucial for several reasons
• It determines the final mechanical properties and visual appearance of the part.
• Controlled cooling rates prevent potential issues such as warping, shrinkage, and distortions in the finished part.
• Proper cooling ensures uniform solidification throughout the part, reducing internal stresses and enhancing structural integrity.
Ejection
Once the material within the mold has sufficiently cooled and solidified, the mold opens, and the part is ejected from the mold cavity. Ejection mechanisms, which can include pins, ejector plates, or other mechanisms, are employed to safely and effectively remove the part from the mold.
Ejection is the final phase of the injection molding process and holds significant importance.
• It must be executed with precision and care to prevent any damage to the newly formed part. Delicate or complex parts require careful ejection to avoid any deformation.
• Proper ejection mechanisms and designs ensure that the part is cleanly and completely removed from the mold. Any residual material or sticking could lead to defects in subsequent runs.
• Successfully ejected parts are ready for further processing, assembly, or quality control checks. This phase marks the separation of the part from its mold, and any post-processing steps can commence.
Hydraulic Injection Molding Machines
Hydraulic injection molding machines are the most traditional and widely used type of machines in the industry. They rely on hydraulic systems to generate the necessary force for mold clamping and material injection.
In hydraulic machines, a hydraulic pump generates the power needed to operate the machine. When the machine is activated, the hydraulic pump forces hydraulic oil into cylinders to drive the machine’s various functions, including mold clamping, material injection, and ejection.
Electric Injection Molding Machines
Overview: Electric injection molding machines are known for their precision and energy efficiency. They use electric servo motors to drive the machine’s functions.
How They Work: Electric machines rely on electric servo motors to precisely control the movements of the injection unit, mold clamping, and ejection. These motors can quickly and accurately adjust their speed and torque, making them highly precise.
Hybrid Injection Molding Machines
Hybrid injection molding machines combine the best of both hydraulic and electric technologies to provide efficiency and flexibility. They are becoming increasingly popular in the industry.
In hybrid machines, hydraulic systems are used for clamping and ejecting functions, while electric servo motors control the injection process. This combination optimizes energy consumption and precision.
Choosing the Right Injection Molding Partner
Selecting the ideal injection molding service provider is a pivotal decision that carries substantial implications for the success of your project, whether you’re a budding startup introducing a new product or an established firm streamlining production processes. To make an informed choice, consider the following key tips and factors:
Expertise and Experience
Begin by seeking a partner with a substantial track record and extensive experience in injection molding, particularly within your specific industry or niche. Scrutinize their portfolio for evidence of past projects akin to your own, and inquire about their proficiency in materials, tooling, and design for manufacturability. Don’t hesitate to request references or case studies to glean insights into their track record of accomplishments.
Quality Assurance
Quality control is paramount. Ascertain that your prospective partner maintains a robust quality control process, one that guarantees consistency and compliance with industry standards. Probe into their quality control protocols, encompassing inspection, testing, and certification procedures, and verify if they hold pertinent certifications such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific credentials. Delve into their history of delivering defect-free components to further bolster your confidence.
Production Capacity
Adequate production capabilities are vital to meet your volume requirements. Assess whether the provider possesses the requisite machinery and infrastructure, commensurate with your project’s scale and intricacy. Seek clarity on production lead times and their capacity to scale up production should the need arise. Unearth any potential production bottlenecks to preempt any hindrances.
Technology and Innovation
In an ever-evolving landscape, align yourself with a partner that keeps pace with the latest in injection molding technologies and innovations. Inquire about their investments in modern machinery and equipment. Ascertain if they offer value-added services such as design optimization or prototyping. Explore their readiness to embrace sustainability and eco-friendly practices, should these align with your project’s objectives.
Cost and Pricing Transparency
While cost is a pivotal factor, it must be supplemented by transparency and clarity in pricing to preclude unforeseen expenses. Solicit detailed quotes that encapsulate all cost facets, including tooling, materials, labor, and potential extras. Scrutinize their approach to cost management and any cost-saving strategies they may proffer. Eschew providers with opaque fee structures.
Communication and Collaboration
A partnership thrives on open channels of communication and a collaborative ethos. Gauge their responsiveness to inquiries and their willingness to engage in detailed project discussions. Confirm the availability of a dedicated project manager or point of contact and assess their adaptability to accommodate design alterations or impromptu adjustments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this comprehensive guide has illuminated the critical facets of injection molding, emphasizing its pivotal role in modern manufacturing. We’ve explored the intricacies of the injection molding process, the various types of machines available, and the essential criteria for choosing the right partner. The key takeaways highlight the significance of injection molding as a cost-effective, precise, and versatile method for producing high-quality parts at scale. Armed with this knowledge, readers are empowered to make informed decisions and drive innovation in their manufacturing endeavours. As you embark on your journey in this field, remember that injection molding is not just a process; it’s a gateway to efficient, precise, and innovative manufacturing.